
As every month, we bring you a new article from our corporate blog. This time we are going to talk about the most effective and natural water purification and treatment system: reverse osmosis. A few months ago, we dedicated an article to discussing this system in the industry and its applications, do you remember? Today, we want to go a little further and delve into certain aspects such as: What is reverse osmosis? What does it consist of? What sets it apart from normal osmosis? If you join us, let’s get into it.
Naturally Effective
Reverse osmosis is a water filtration process that works by pressure, guiding water through a semi-permeable membrane. The force of this pressure exerted on the water causes it to pass through the membrane, separating pure and clean water from any possible contaminants that may be present in it.
It is a natural process that has proven to be highly effective, making it the most widely used in industrial sectors.
But… how does it work?
Okay, the above was a brief summary. Let’s try to explain a little better the different elements involved in the process:
- We have our wastewater (obtained as a result of the industrial process in question), a solution rich in contaminating molecules, making this water unfit for human consumption and, in many cases, for reuse in other processes.
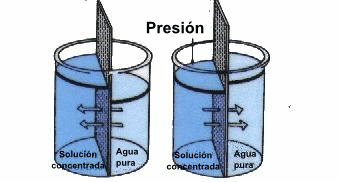
- Well, as we’ve said, in the reverse osmosis process, what we do is apply pressure to this water, causing it to pass through the so-called osmosis membrane, a semi-permeable membrane that separates these contaminating molecules from the water itself.
- This pressure exerted on the wastewater must exceed the so-called osmotic pressure, one of the colligative properties of any solution, allowing the solution to be retained on the pressure side of the membrane, and the pure solvent (potable or reusable water) to pass through.
Why do we say it’s reverse?
Good question. Obviously, if we keep talking about reverse osmosis, it’s because there is normal osmosis. The process of normal osmosis that occurs in nature is as follows: In a solution, it is usual for the solvent (water) to move from an area of low concentration of the solution to an area of high concentration. This movement through the membrane generates a force, the so-called osmotic pressure.
As we have already seen, reverse osmosis is nothing more than the application of external pressure that breaks the natural osmotic pressure of the solution, causing the flow to reverse and, therefore, in a contaminated wastewater solution, pure water passes through the semi-permeable membrane, separating from the waste.
Now that you have a little clearer what reverse osmosis is and how it works, you’ll be glad to know that at Eneragua, we use this purification technique for industrial installations of both brackish water (from the public network, underground or surface aquifers) and seawater (from beach wells).
Each of these types of water has its own characteristics. Brackish water, as its name implies, is rich in salts and has a low concentration of organic matter and pathogens. Seawater, on the other hand, has a low concentration of suspended solids, a high amount of organic and biological matter, and a high concentration of mineral salts.
The great benefit of reverse osmosis is that it is a purely natural process, with no direct intervention of chemical assets, making it tremendously environmentally friendly. Moreover, it requires minimal energy consumption to carry it out. All advantages.
Principio del formulario






